Basic Concept
Energy is carried by electric current
Electric current is the rate flow of electric charge past a point.
I=\frac{Q}{t}The unit of charge is Coulomb (C), and the unit of current is Ampere(S.I. Unit)
Charge is Quantised: charge values are not continuous; they are discrete. All charges are multiples of charges of
1e=-1.6\times10^{-19}Potential difference: If two points have a potential difference of 1V if the work required to move 1C of charge between them is 1 joule
W=VQ\\
P=VI; P=I^2R; P=\frac{V^2}{R}Cells in the circuit give energy to charges, which transfer to useful energy and heat.
The e.m.f. is the total work a battery does per unit charge when the unit charge goes around a complete circuit.
Conductors
Electrons move in a specific direction when p.d. is applied across a conductor, causing current.
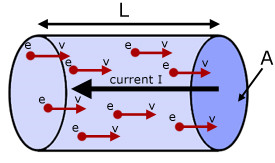
I=nAvq
Where I = Current, A = Arear, v = velocity of the electron, n = number density, q = the charge carried.
Resistance and Resistivity
Resistance is the opposition to the passage of current within a component. The unit of resistance is Ohm
R=\frac{V}{I}R=\rho \frac{L}{A}1 ohm is the resistance when 1-volt drives 1 ampere through.
I-V Characteristic
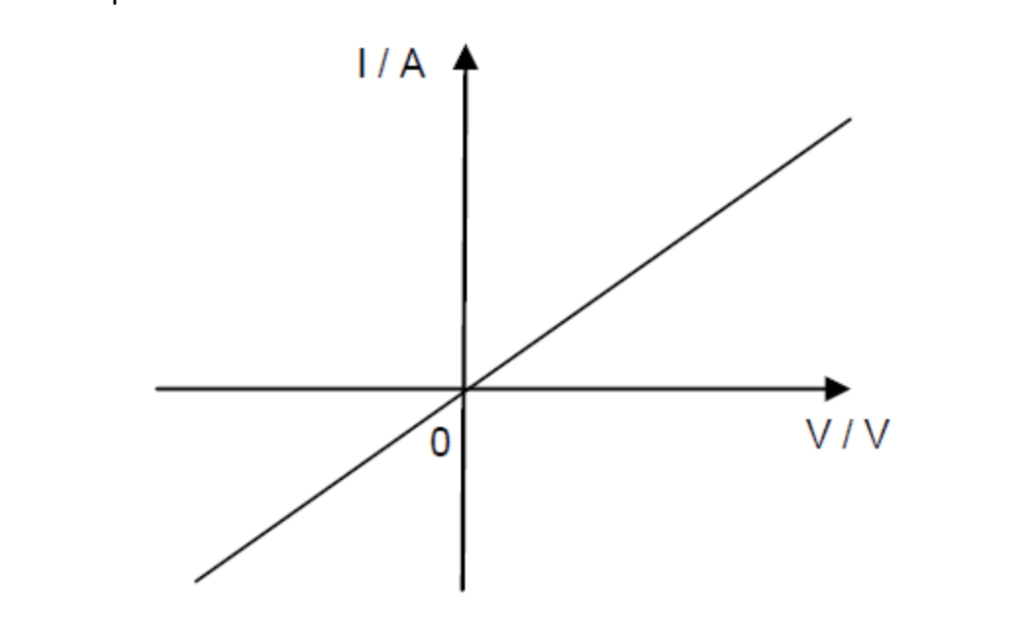
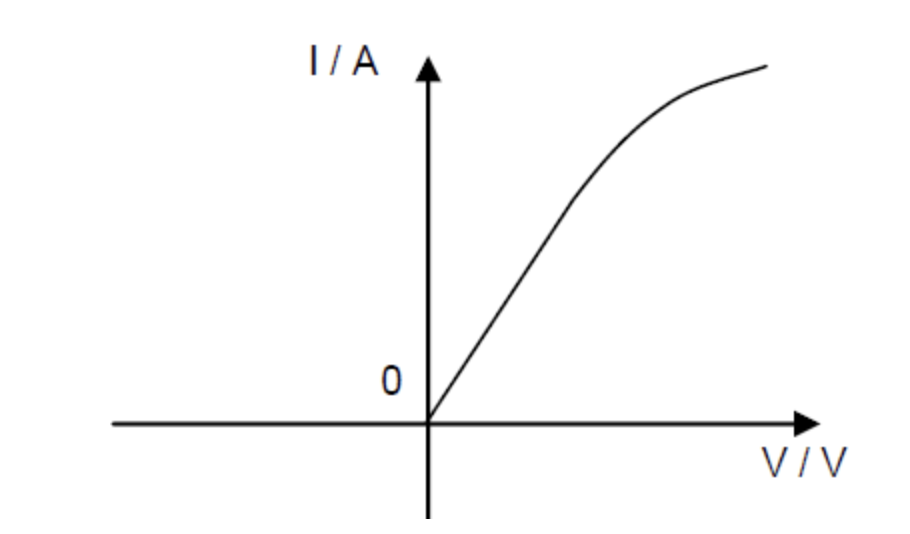
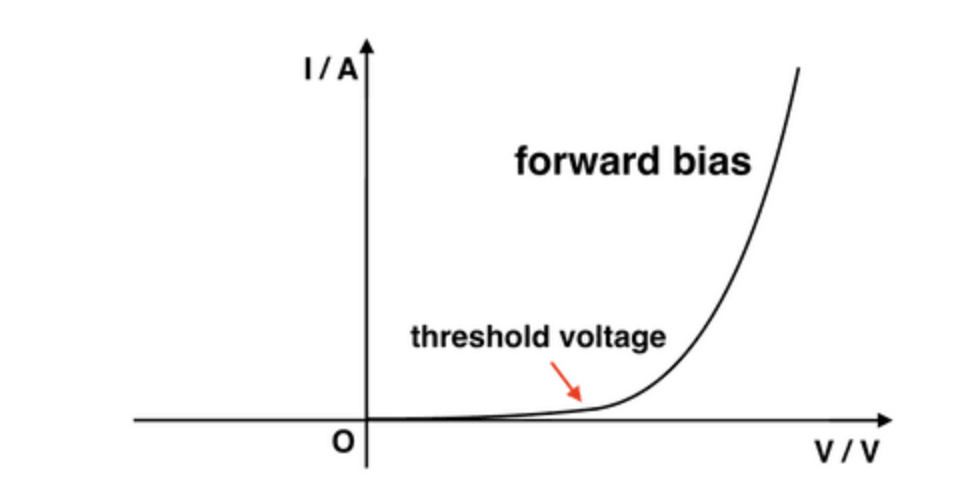
D.C. Circuit
Kirchhoff's Law
First Law
The sum of current into a junction = Sum of current out of that junction
It's about the conservation of charges
Second Law
Total e.m.f. in any loop = Total p.d. in that loop
It's about conservation of energy
Resistance in Series and Parallel
Series
R=R_1+R_2
Parallel
\frac{1}{R}=\frac{1}{R_1}+\frac{1}{R_2}Potential Divider
The potential divider divides the voltage into smaller parts
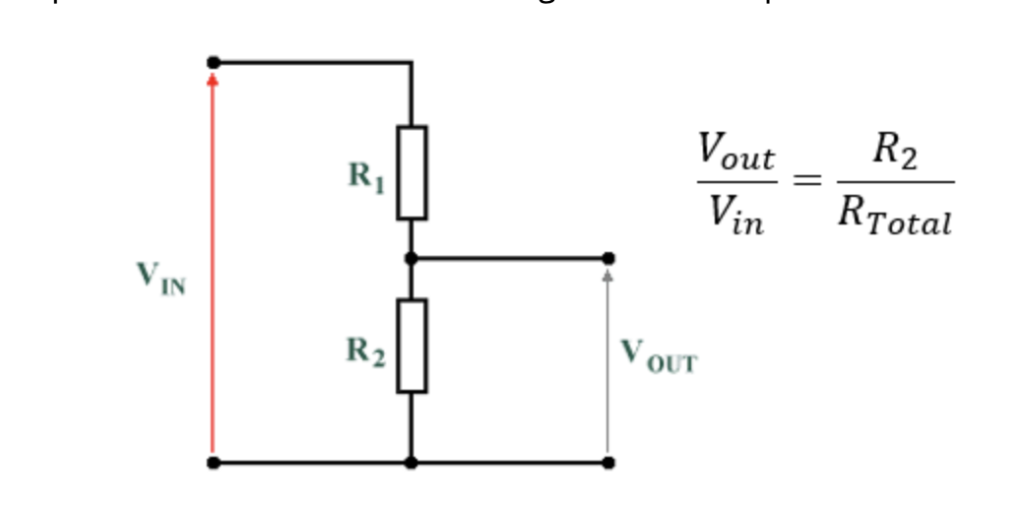
Potentiometer
A potentiometer is a continuously variable potential divider used to compare potential differences.
If the galvanometer needle didn't deflect, the current passed through it = 0; thus, it is the same p.d.
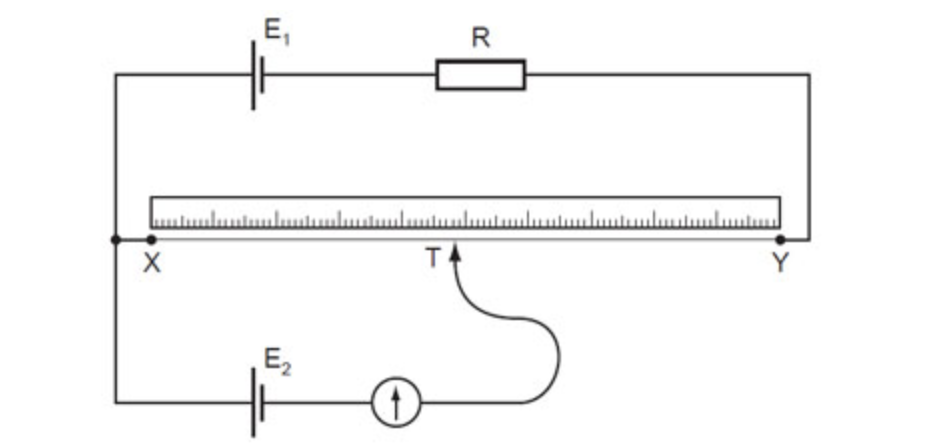
\frac{E_1}{E_2}=\frac{L_{XY}}{L_{XT}}
Comments NOTHING